Design
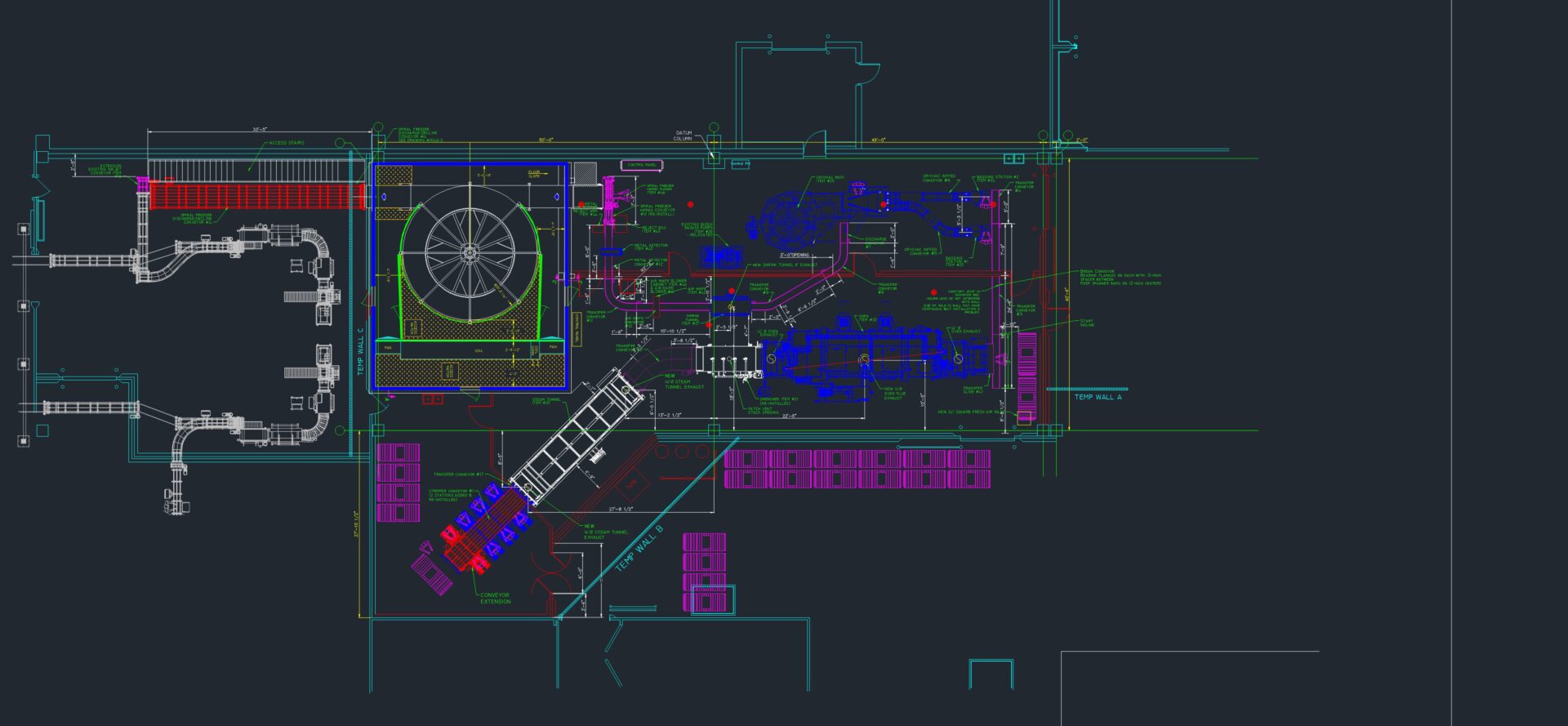
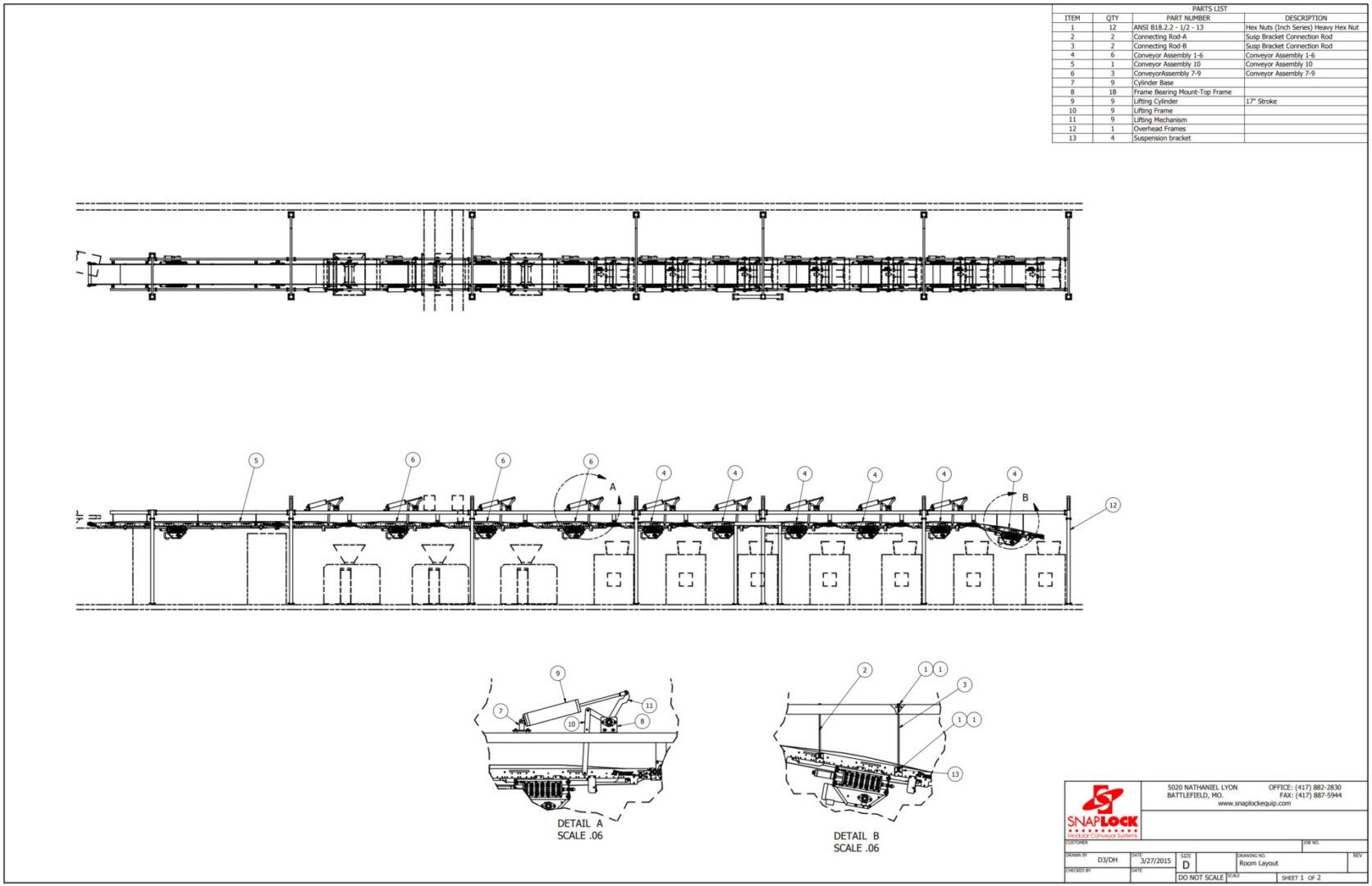
Mechanical equipment design is a specialized field that involves the creation and development of machinery and mechanical systems tailored to specific industrial or commercial applications. Engineers in this discipline focus on designing equipment that meets functional requirements while adhering to safety, reliability, and regulatory standards. The process begins with understanding the operational needs and constraints of the equipment, followed by conceptualization, detailed design, and prototype development. Factors such as materials selection, mechanical principles, and manufacturing processes are carefully considered to optimize performance, durability, and cost-efficiency. Computer-aided design (CAD) software plays a crucial role in modeling and simulating designs to refine performance and ensure compatibility with other systems. Throughout the design process, engineers collaborate closely with stakeholders, including manufacturers and end-users, to incorporate feedback and ensure the final product meets or exceeds expectations. Effective mechanical equipment design not only enhances productivity and efficiency but also contributes to innovation and technological advancement in various industries.
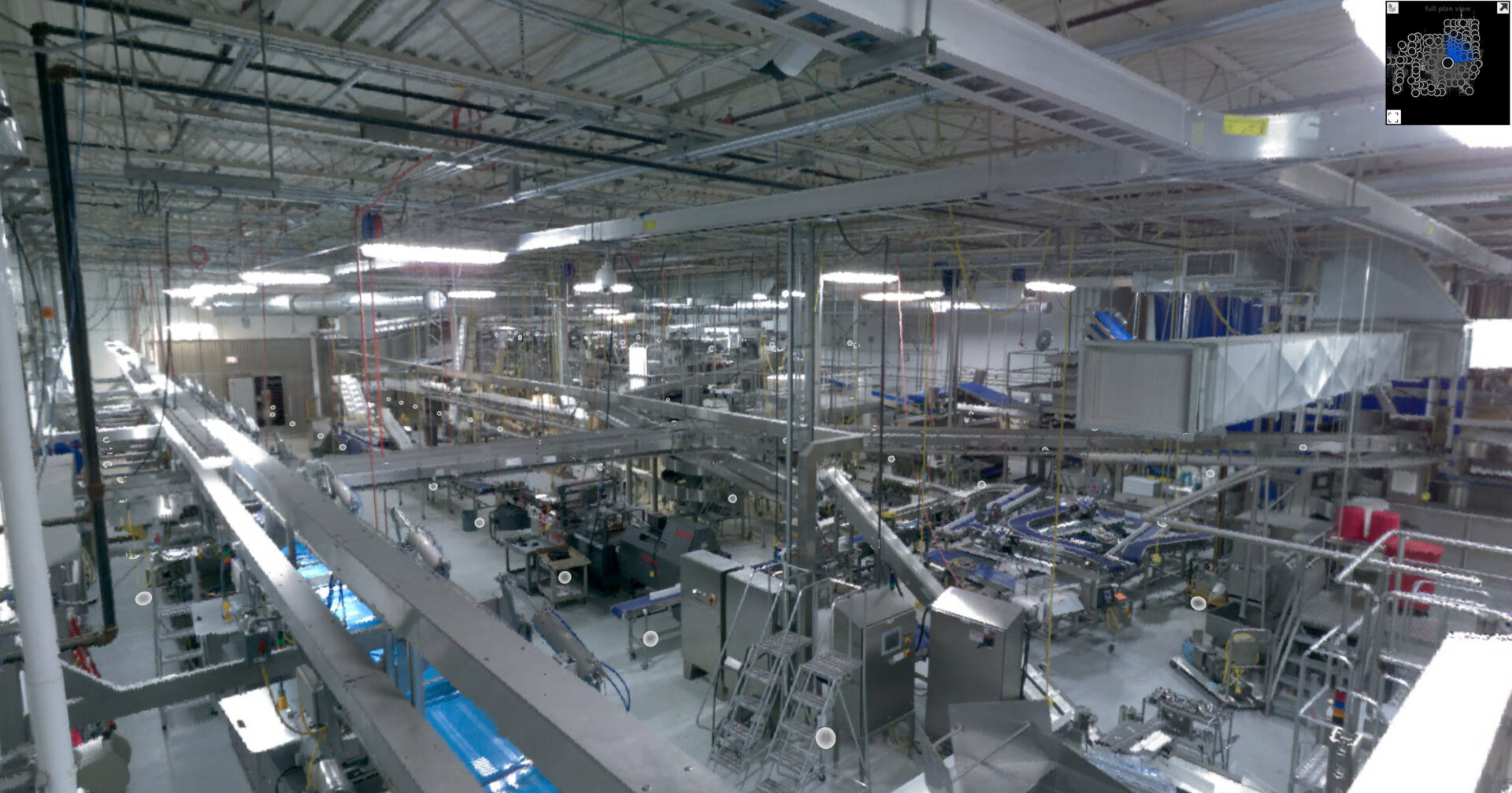
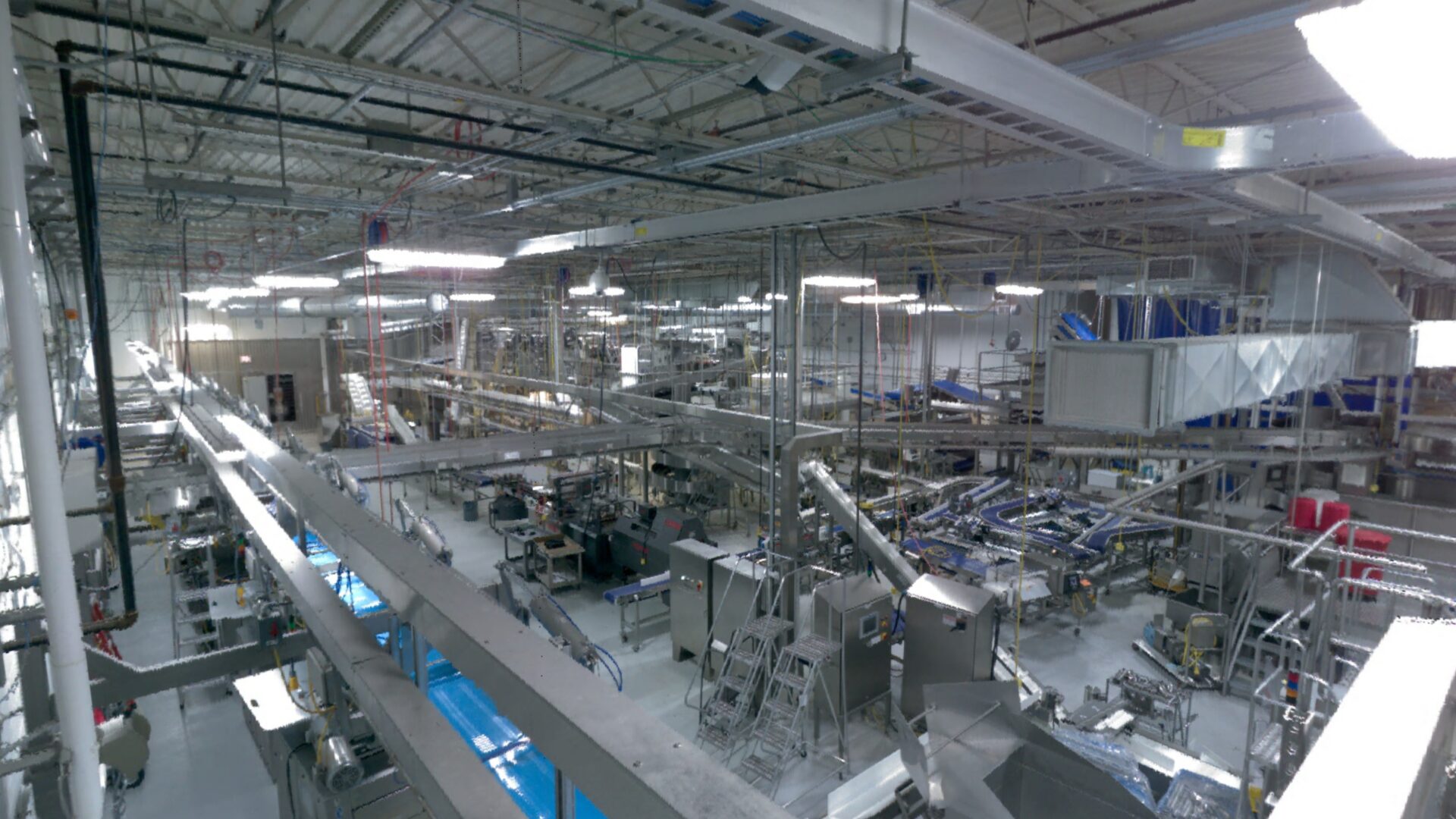
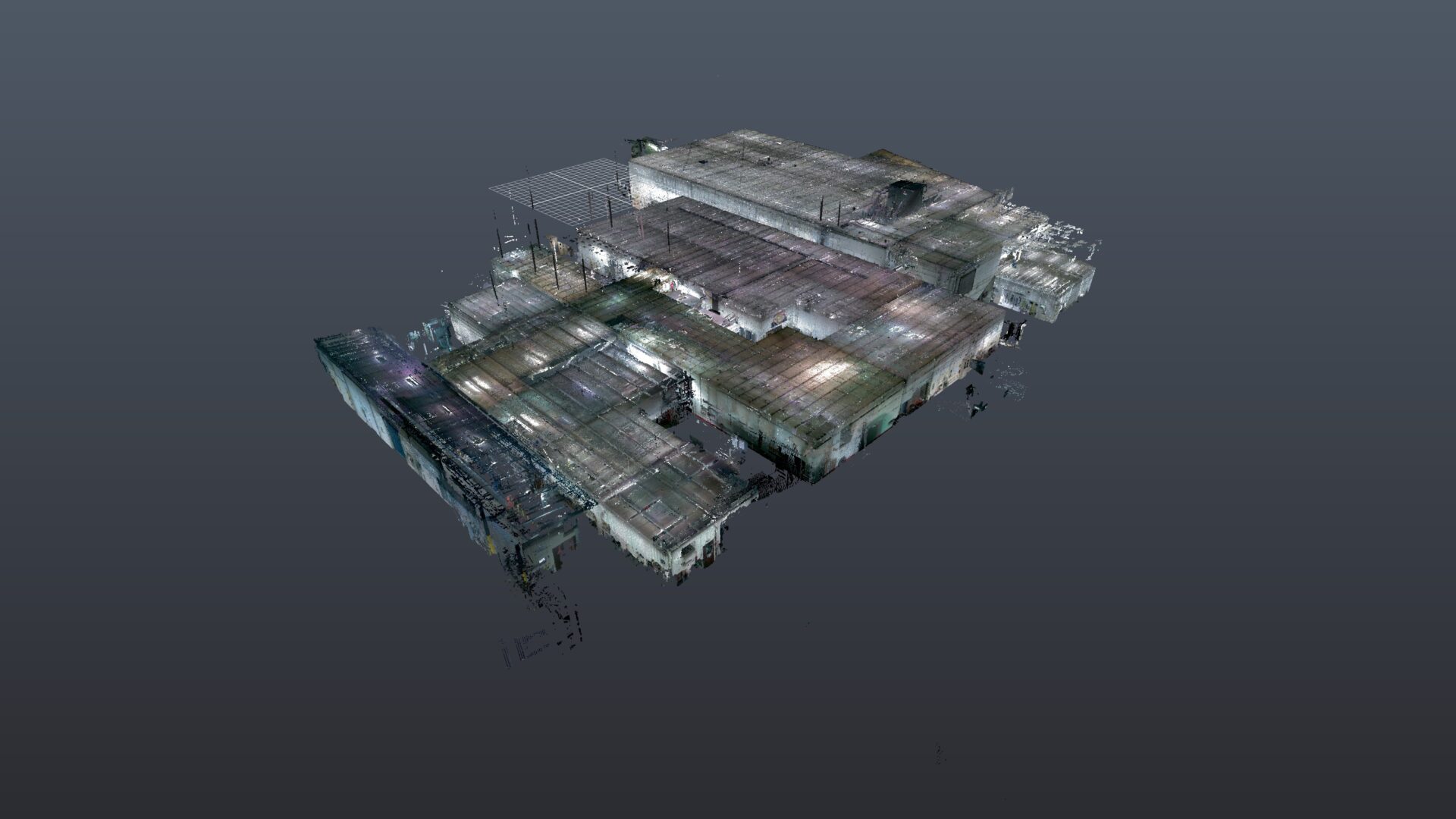
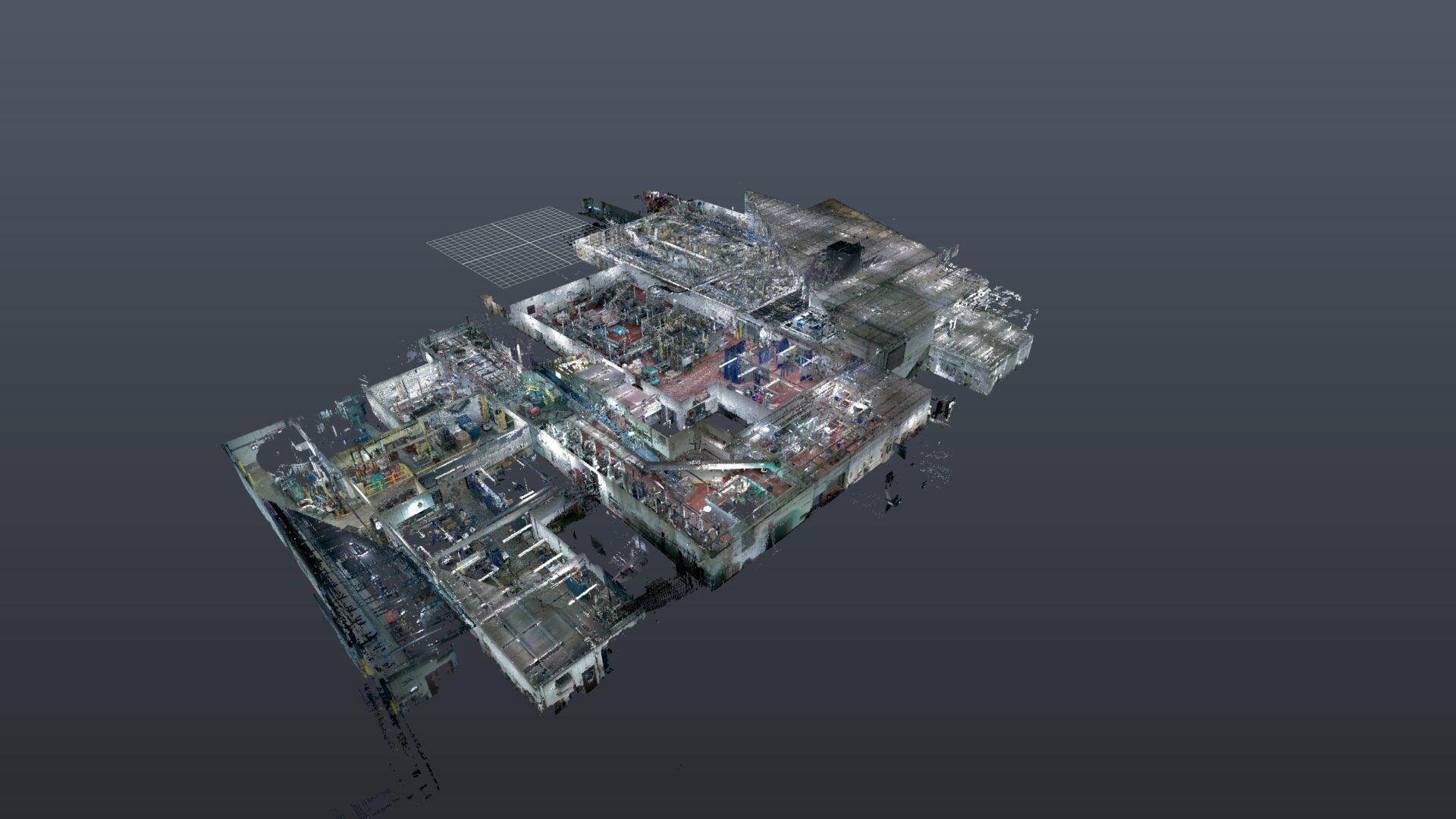
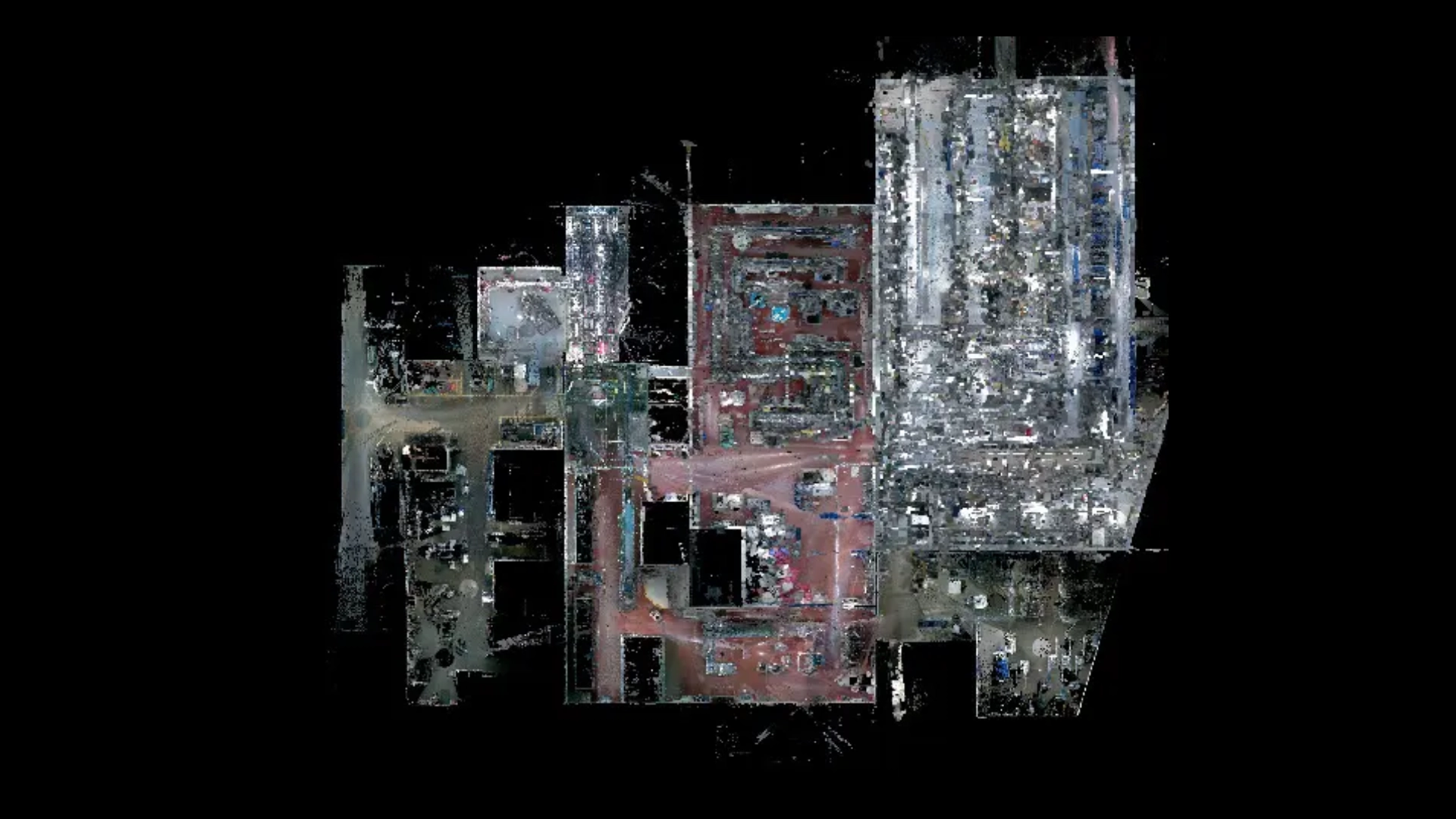
Snap Lock, Inc. offers 3D point cloud scanning service.
The 3D Point Cloud Scans can be used as standalone or inserted into 2D and 3D CAD drawings and models.
- Document Line and plant changes and updates.
- When used in conjunction with 3D CAD Modeling we can document existing building, equipment, piping, ductwork and other potential obstructions for proper routing of conveyors and other new or proposed equipment.
- CAD software and the knowledge of the software are required for most file viewing and manipulation of the 3D point cloud scans
What is Point cloud scanning?
Point cloud scanning is a method used in various fields, including surveying, engineering, architecture, and digital modeling, to capture the three-dimensional coordinates of points on the surface of an object or environment. It involves using specialized equipment such as LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) or photogrammetry to collect data.
Here's how it generally works:
- Data Acquisition: A device, such as a LiDAR scanner or a camera system, is used to capture the geometry of an object or environment. LiDAR scanners emit laser pulses and measure the time it takes for the light to return after hitting an object, thereby determining distances and creating a point cloud. Photogrammetry uses overlapping photographs to create a 3D model.
- Point Cloud Generation: The collected data is processed to create a point cloud, which is essentially a large collection of points in three-dimensional space that represent the surface of the scanned object or environment. Each point in the cloud has its own set of coordinates (x, y, z) representing its position in space.
- Post-Processing: The point cloud data may undergo post-processing to remove noise, outliers, and other artifacts that may have been introduced during the scanning process. Additionally, it may be filtered or segmented to isolate specific features or objects within the point cloud.
- Analysis and Visualization: Once the point cloud data is processed, it can be analyzed, visualized, and manipulated using various software tools. This data can be used for tasks such as creating accurate 3D models, performing measurements, detecting changes over time, or generating digital twins of real-world objects or environments.

Project Management
Project management is the discipline of planning, organizing, and executing projects within defined constraints to achieve specific goals. It involves initiating a project, setting clear objectives, identifying stakeholders, and establishing a project team with assigned roles and responsibilities. Throughout the project lifecycle, project managers monitor progress, manage resources, mitigate risks, and ensure adherence to timelines and budgets. Effective communication and collaboration are essential, as project managers facilitate teamwork and coordinate efforts to deliver the desired outcomes. They also employ various tools and methodologies to streamline processes and optimize efficiency. Ultimately, project management aims to achieve successful project completion by balancing scope, time, cost, and quality while meeting stakeholders' expectations and organizational objectives.
Site Survey
A food plant site survey, a crucial initial step in planning, development, and layout of food processing facilities, is conducted by a team of experts well-versed in Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP), product flow, and rates. Our survey aims to gather comprehensive data about the proposed needs, while also examining utilities infrastructure availability—water, electricity, steam, pneumatic, and drains—essential for the efficient operation of the plant. This thorough survey lays the foundation for informed decision-making, ensuring the successful establishment of a safe and efficient food processing facility.


Project Scoping
Project scoping is a critical phase that defines the entirety of a project, setting its boundaries, objectives, and deliverables. It involves outlining the purpose of the project, identifying stakeholders, and determining the resources required, including budget and timeline constraints. During this phase, key project requirements and constraints are documented to ensure alignment with organizational goals and client expectations. Clear scoping allows for the establishment of project priorities and a roadmap for execution, helping to manage risks and allocate resources efficiently. Effective project scoping lays the groundwork for a successful project outcome by providing a clear understanding of what needs to be achieved and how it will be accomplished. Regular reviews and adjustments during this phase ensure that the project remains on track and adaptable to changes as needed.
Research & Development
Research and Development (R&D) is a systematic process of inquiry and experimentation aimed at creating new knowledge, products, or processes. It plays a pivotal role in advancing technology, innovation, and competitiveness across industries. R&D encompasses activities such as basic research to expand scientific knowledge, applied research to solve specific problems, and development to translate findings into practical applications. Organizations invest in R&D to stay ahead of market trends, improve existing products, or create entirely new ones that meet evolving consumer needs. It involves interdisciplinary collaboration, rigorous testing, and continuous refinement to ensure the feasibility, effectiveness, and safety of innovations. Successful R&D efforts often lead to breakthroughs that drive economic growth, enhance quality of life, and contribute to sustainable development on a global scale.